Macular Degeneration Explained
Great read for friends/family to better understand the diagnosis their loved one has.
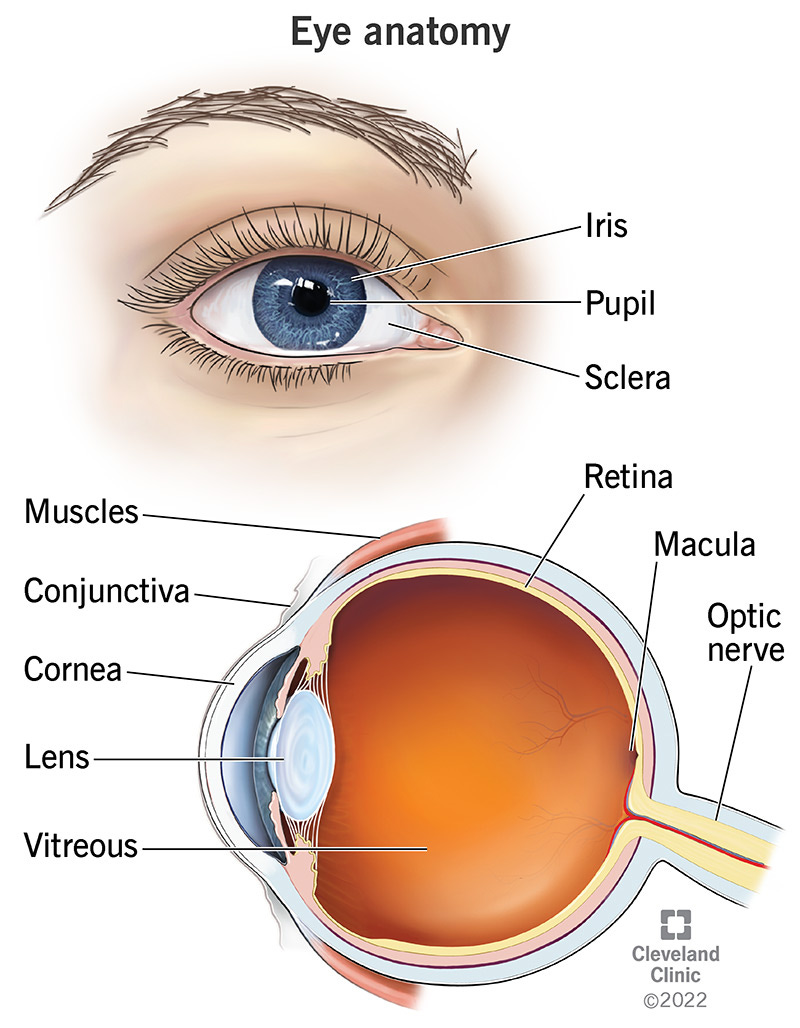
Macular Degeneration is categorized as an age-related disease with two subtypes. At its core, AMD (Age-related Macular Degeneration) is a problem with one’s retina, more specifically, the macula (See diagram below)
With AMD, central vision is lost while peripheral stays intact. A great example would be to “imagine you are looking at a clock with hands. With AMD, you might see the clock’s numbers but not the hands.”
The first subtype of AMD is Dry AMD. This is the most common type, with around 80% of patients having this type. Parts of the macula get thinner with age and tiny clumps of protein, called drussen, form. The patient slowly loses their central vision due to the clumps of protein.
The second subtype of AMD is Wet AMD. This type may be less common, but it is more severe. This happens when abnormal blood vessels grow beneath the retina, start to leak blood or other fluids and this scars the retina. This happens much quicker than dry AMD.
Risk factors for AMD can be found below.
Those who eat a diet high in saturated fat.
Those who are overweight.
Those who smoke cigarettes and/or vapes.
Are over 50 years old.
Have hypertension.
Have a family history of AMD.
Have a question? Leave a comment below!
The information provided on the site is for educational purposes only and does not substitute for professional medical advice.